
Conservation
of Energy
On An Inclined Plane
BlackBoard Notes
======================= Photo - Click for a Larger Version =============================
======================= First Board Section =============================
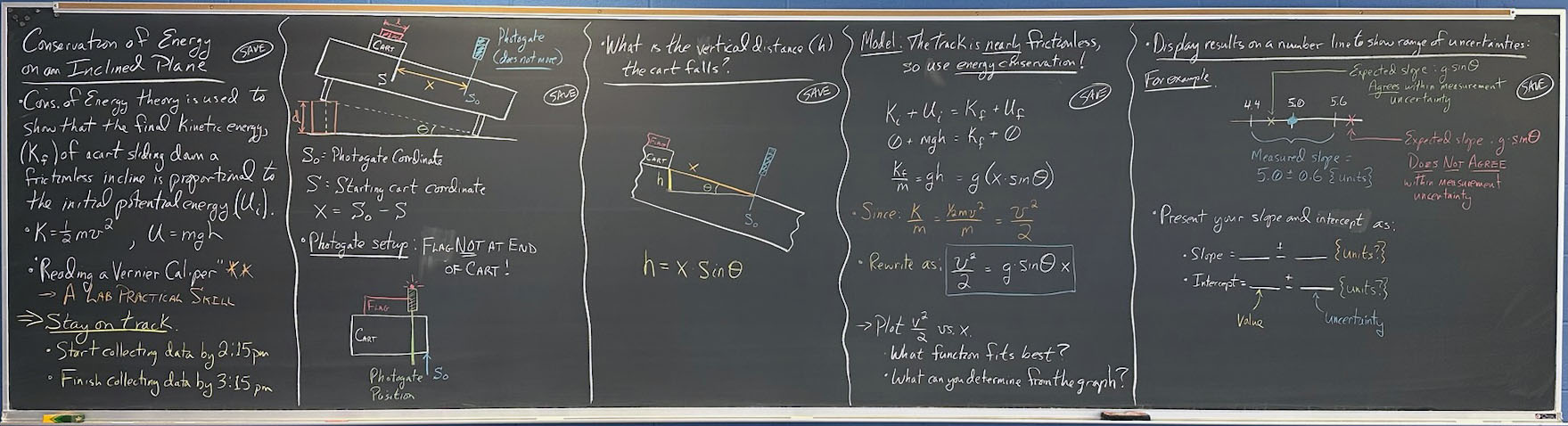
- Conservation of energy theory is used to show that the final kinetic energy, Kf of a cart sliding down a frictionless incline is proportional to the initial potential energy, Ui
- K = ½mv2, U = mgh
- "Reading a Vernier Caliper" (a lab practical skill!)
- Stay on track!
- Start collecting data by 2:15 pm
- Finish collecting data by 3:15 pm
======================= Second Board Section =============================
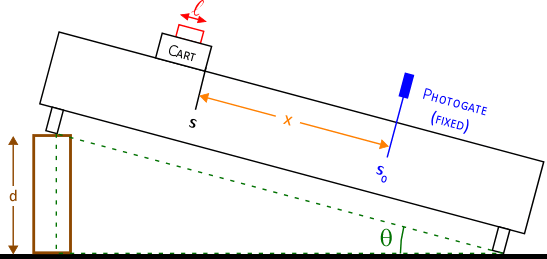
- so = Photogate coordinate
- s = Starting cart coordinate
- x = so - s
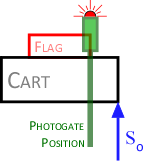
- Photogate Setup - flag NOT at end of cart!
======================= Third Board Section =============================
- What is the vertical distance (h) the cart falls?
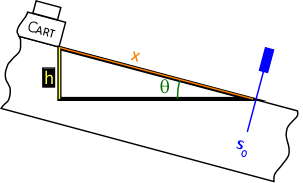 h
= x·sinθ
h
= x·sinθ
======================= Fourth Board Section =============================
- Model: Track is nearly frictionless, so use energy conservation:
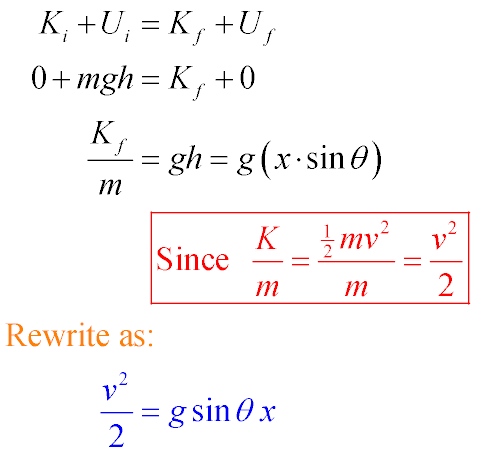
- Plot v2/2 vs. x. What function fits best?
What can you determine from the graph?
======================= Fifth Board Section =============================
- Display results on a number line to show range of uncertainties:
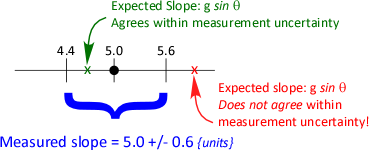
- Present your slope and intercept as:
- slope = ____ +/- _____ {units?}
- intercept = ____ +/- _____ {units?}
- (where first blank is the value, second blank is the uncertainty)
Return to Setup
|
Revised: 07 Jul 2025
|
Canton, NY 13617
|


 h
= x·sinθ
h
= x·sinθ