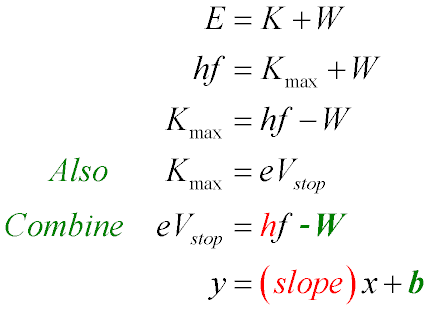

The Photoelectric Effect
BlackBoard Notes
======================= Photo - Click for a Larger Version =============================

======================= First Board Section =============================
- What affects the energy of electrons ejected from a metal surface: the intensity of light {wave theory} or frequency/color {photon theory}?
- Inside the photoelectric head:
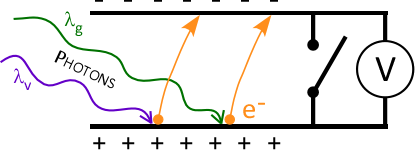
- Electrons ( e– ) absorb energy and can be ejected
======================= Second Board Section =============================
- Photon Model:
- Photons carry energy:
E = hf
- (Point to parts of first equation and label that K is kinetic energy, W is e– binding energy; see blackboard photo for tips)
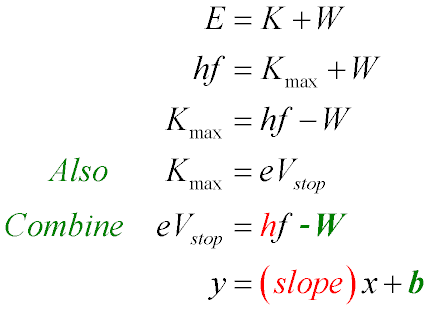
(Where W ⇒ electron binding energy; h ≡ Planck's constant)
======================= Third Board Section =============================
- Kaleidagraph: Plot eVstop vs. f
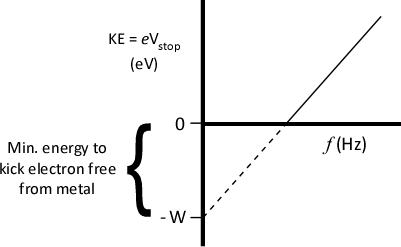
- Create custom fit in Kaleidagraph
- Refer to "Finding the Best-Fit Function"
- Calculate h & W (and their uncertainties).
- Units – electron-volt (eV): Amount of K gained (or lost) by an electron accelerating through an electric potential difference of 1 volts.
- If V = 5 volts, what is K?
======================= Fourth Board Section =============================
- Wave theory:
- Kmax depends on light intensity (brighter light → greater ejected energy)
- Use "Relative transmission" slide
- Regions with 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100% transmission
- Notes:
- Use yellow and green filters for yellow and green lines only!!
- The mercury lamp is HOT!
- Don't turn off Hg lamp until you are finished with lab.
- Do turn off multimeter & flashlight!
Return to Setup
|
Revised: 09 Jul 2025
|
Canton, NY 13617
|